In human bodies, collagen is as important as the heart in our body. It helps us keep young and healthy. When we are born, the collagen is at max, but as we age, collagen deficiency happens, and we get older. However, aging can be slowed down by taking collagen supplements. But the problem here is there are 28 kinds of Collagen in our body, and it's very necessary to understand which kind does what so we don’t overdose on the other kind. So, read on to keep yourself young and healthy.

Figure-no-1-Types-of-Collagen
➔ Checklist
1.What is Collagen?
2.How Does Collagen Function in the Body?
3.Varieties of Collagen: What Are the Different Types?
“Just like our hairs grow naturally, Collagen is a protein that our body makes regularly.”
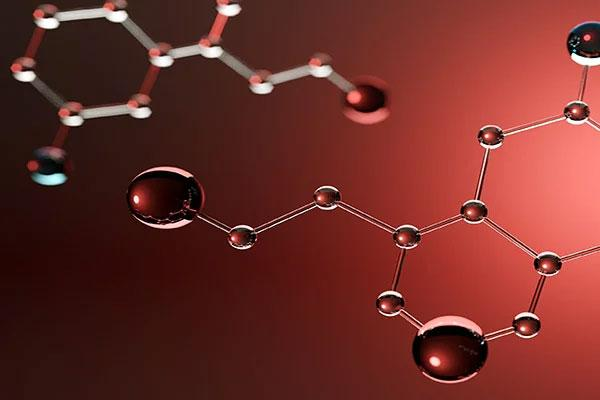

Figure no 2-what-is-collagen
It is amazing to note that in the human body, about 30% of the protein ratio is owned by Collagen, and as compared to whole body mass, proteins make up 14~16%. Collagen is present everywhere, just like air on Earth; for example, you can find it in organs, intestine linings, bones, skin, and every other part of the human body.
2) What does Collagen do in the body?
The following are the roles of Collagen in our body:

Figure no 3 What is the role of collagen in the body.
✓ Within the skin - keeps soft, elastic, strong, and wrinkle-less.
✓ Upper layer on organs & intestines - act as a protective layer
✓ Inside bones - helps in bone formation, increases density, and slows osteoporosis
✓ In Joints - helps in their formation when they act as attachment points & shock absorbers
✓ Nails - Collagen makes up keratin, which then makes nails. So, Collagen is responsible for nail growth and health
✓ Hairs - The primary protein, keratin, in hairs, comes from a certain amino acid of Collagen, so basically, Collagen makes hairs. Plus, the dermis layer, in which hair follicles ( roots ) are present, is majorly made of Collagen.
✓ Blood Vessels - Collagen fibers are present beneath the inner layer of blood vessels in the form of a network. Moreover, they provide structural support, and during an injury, they act as a magnet for healing agents and help repair.
✓ Between muscle strands - act as a glue for muscles, keeping them bound together and providing tissue elasticity. They also function as a medium to transmit contractile force from muscles to the skeleton ( bones, tendons, ligaments ).
3) What are the different types of Collagen?
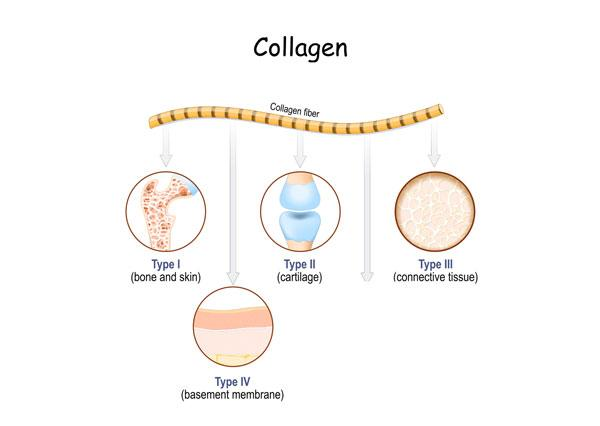
Figure no 4-What-are-the-different-types-of-Collagen
Scientists have discovered well over 28 kinds of Collagen and they are classified based on their building materials, structural arrangement, and functions they perform.
From these 28 types, there are 5 Collagens that have the most effect, such as;
a) Collagen Type I ( most abundant )
b) Collagen Type II
c) Collagen Type III ( most abundant )
d) Collagen Type V
e) Collagen Type X
a) Type I Collagen & its Uses
“Type I Collagen is a long, triple-helical protein, and it is made of three amino acids: glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. The glycine residues form the core of the triple helix, while the proline and hydroxyproline residues provide flexibility and strength.”
You can estimate the significance of Type I Collagen from its 1st position in the naming category because it consists of 90% of all the Collagen in the human body, especially in skin, bones, and connective tissues ( tendons, ligaments, cartilage ).
➔ Uses of Type I Collagen
As Type I Collagen is abundant in skin and bones, you can estimate its main function is to keep the skin young and maintain the strength of bones - the details of which are given below;
✓ Skin health: If you have wrinkles, sagginess, or roughness on your skin, then its main problem is the deficiency of Type I Collagen.
✓ Muscle contraction: Type I Collagen is also important for muscle contraction. It helps to connect muscle fibers and allows them to contract and relax.
✓ Blood vessel formation: Type I Collagen is also important for blood vessel formation. It helps to form the walls of blood vessels and keeps them strong and healthy.
✓ Wound healing: Type I Collagen is also important for wound healing. It helps to form a scab over the wound and provides a framework for new tissue growth.
✓ Cartilage repair: The joints in the human body are made of a cushy substance called cartilage, and this cartilage is made of primarily Type I Collagen. Cartilage acts as a shock absorber and friction-decreasing point between two bones.
✓ Bone formation: Without bones, we are like a long piece of cloth lying on the floor. Our body manufactures bones mostly from Type I collagen. So, more Type I Collagen means better bone production, faster healing, and stronger bone structure.
b) Type II Collagen & its Uses
“Type II Collagen is made up of three long chains of amino acids that are intertwined together to form a triple helix. The triple helix provides type II Collagen strength and flexibility.”
It is present most abundant in the joint's cartilage and is responsible for delivering resilience and flexibility. Type II Collagen supplements are typically made from chicken or bovine cartilage.
➔ Uses of Type II Collagen
✓ Joint health: Type II Collagen is most abundant in cartilage, so it makes sense that taking its supplements will help treat bone & joint diseases like osteoarthritis, etc. It also helps relax from joint pain and adds cushiness to joints for better movement.
✓ Skin health: Some research has shown that type II Collagen supplements can lessen the appearance of wrinkles and age spots and help improve skin elasticity.
✓ Gut health: Some research studies have shown that type II Collagen supplements can help to protect the inner/outer surface of the gut and improve digestion and absorption of nutrients.
✓ Immune system function: Type II Collagen supplements are also sometimes used to help the immune system fight against diseases, which results in faster recovery from diseases.
c) Type III Collagen & its Uses
“Structurally, Type III Collagen is formed from three identical alpha chains, making it a homotrimer, unlike Type I Collagen, which consists of two alpha1 chains and one alpha2 chain.”
When it comes to Type III collagen, it is the 2nd most abundant Collagen category in the human body. It is widely distributed across diverse tissues like the bowel, blood vessels, uterus, skin, and organ linings. According to the data from various parts of the human body, it is recorded the Type I to Type III Collagen ratio is like 4:1 ( skin ), 3:1 ( organs ), etc.
This type of Collagen, which is classified as fibrillar, creates long, thin fibers that provide tissues with strength and flexibility. Plus, it also helps wounds heal faster. Additionally, it maintains the architecture of blood vessels and other organs, aiding their proper functioning.
➔ Uses of Type II Collagen
✓ Joint health: Type III Collagen is not that abundant in bones and cartilage, but it is present and helps support other cartilage types to maintain bone strength and health.
✓ Skin health: Type III Collagen is very abundant in the skin, just like Type I Collagen, and it helps the skin to avoid fine lines, which later become wrinkles. Plus, Type III Collagen forms a structural network beneath the skin to keep the skin tight, but as Collagen is elastic, the skin remains stretchable.
✓ Hair health: Tpye III Collagen provides the raw material for the formation of hairs, so it basically enhances hair growth and strength. Moreover, Type III protein is also found in the scalp where hair roots are present. In short, taking Type III Collagen supplements will help a person with weak hair.
✓ Wound healing: Type III is the second most abundant Collagen protein in muscles & organs, and as you know, Collagen is a natural magnet for healing cells; in case of any injury, Collagen helps form new tissues quickly.
✓ Immunity: Type III Collagen may help to enrich immunity by evoking the production of white blood cells. It is often used in supplements to treat autoimmune diseases and other immune system disorders.
d) Type V Collagen & its Uses
“This Collagen type is classified as fibrillar, weaving into long, cable-like fibers that confer strength and flexibility to tissues - it works with Type I and Type III Collagens, creating the scaffolding for tissues and organs.”
Type V Collagen is not as abundant as the rest of the five major Collagen kinds, but it does perform critical functions such as making the cornea of the eyes, layers of skin& hair, and placental tissue. Operating within the extracellular matrix of diverse tissues, such as the skin, bones, blood vessels, and placenta, it offers vital structural support.
➔ Uses of Type II Collagen
✓ Hair and Nails: It supports the health and robustness of hair and nails.
✓ Eye Health: It's a key component of the cornea, contributing to maintaining the eye's shape and clarity.
✓ Skin Resilience: Type V Collagen assists in sustaining skin health, contributing to its strength and elasticity.
✓ Blood Vessels: Type V Collagen forms the structure of blood vessel walls, contributing to their stability and proper function.
✓ Tissue Formation: Type V collagen helps other collagen types in the manufacturing of various tissues and organ layers, so it helps in their healthy growth.
e) Type X Collagen & its Uses
“Type X Collagen comprises a short triple helix of Collagen flanked by two non-collagenous domains, NC2 and NC1.”
It aids in binding essential minerals, such as calcium, to Collagen fibers, enhancing bone strength - by doing so, it contributes to the robustness of our skeletal system.
Unlike other Collagen types, it doesn't create long fibers but forms a network of shorter fibers. This distinct network provides strength and flexibility to the growth plate and the calcified area of articular cartilage.
➔ Uses of Type II Collagen
The following are some uses of Type X Collagen;
✓ Specialized Role: Even though it's found in smaller amounts, its distinct function in skeletal development highlights its importance.
✓ Transition Signifier: Type X Collagen acts as a marker during bone development, indicating the shift from cartilage to solid bone.
✓ Growth Plate Indicator: Its presence in growth plates signals the crucial transformation that underpins longitudinal bone growth.
✓ Growth Facilitator: By aiding this transition, Type X Collagen ensures bones grow both in length and strength, which are essential for robust bone health and structural integrity.
➔ Conclusion
Collagen manufacturers around the world make specialized supplements that are focused on producing a specific type of Collagen, like Type I or Type II and others. However, it is important to note that some are bovine Collagen manufacturers, some are pig, while others use mixed animal parts - which can be a problem in quality and for some cultures ( pig Collagen is haram in Islam ).
However, we at Yasin aim to manufacture Collagen from all kinds of animals but in specific containers to ensure consumers are getting what they demand. So, if you belong to protein suppliers or Collagen powder suppliers, we can ensure that you get 100% authentic products from us.
Post time: Sep-08-2023